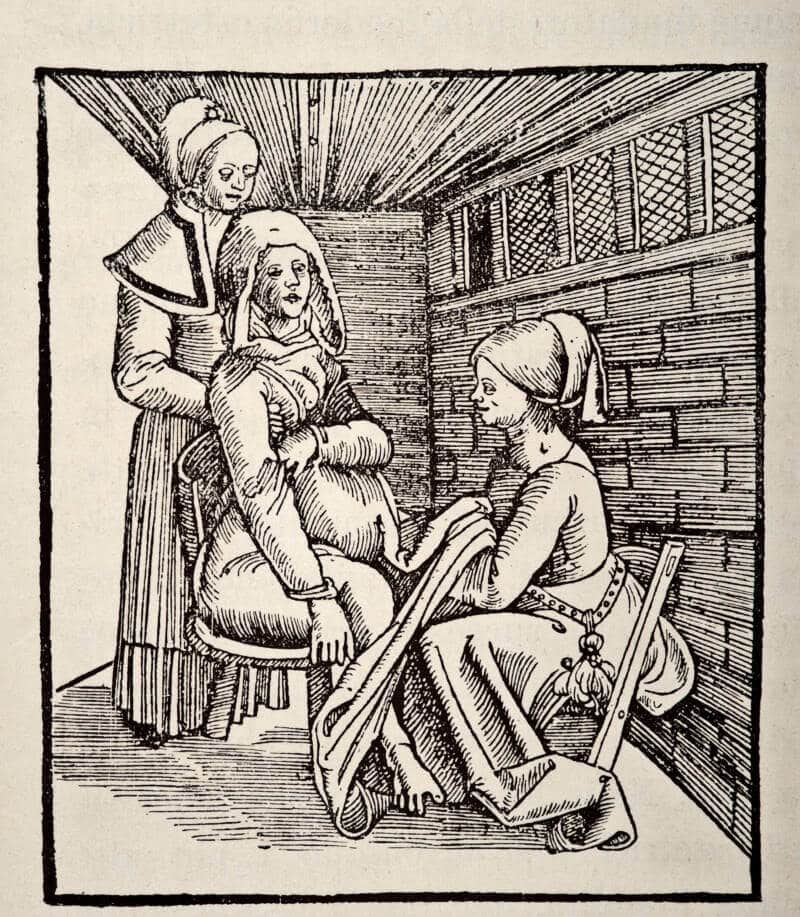
Justine Siegemund, also known as Siegemundin, was a remarkable figure in the history of medicine and obstetrics. Born in the 17th century, her groundbreaking work and influential writings in the field of midwifery have left an indelible mark on the medical community. This article aims to shed light on the life, career, and significant contributions of Justine Siegemund, the first female author of a German medical text.
- RELATED: Dan Bilzerian Net Worth: The Financial Depth of Instagram’s King.
- RELATED: Patrick Mahomes’ wife: Brittany Mahomes the Woman Beyond the NFL Spotlight
- RELATED: John Legend Net Worth: Harmonizing Talent with Financial Acumen
Table of Contents
Early Life and Marriage
Justine Diettrich, born on December 26, 1636, in Rohnstock, Silesia (now Roztoka, Poland), was the daughter of Elias Diettrich, a Lutheran minister. After the death of her father in 1650, Justine pursued her career in midwifery, a decision that would define her life’s work. In 1655, she married Christian Siegemund, and the couple, despite remaining childless, supported each other in their respective professional endeavors.
Embarking on a Midwifery Career
Siegemund’s journey into the world of midwifery began when she personally experienced a prolapsed uterus, leading her to seek knowledge and understanding of obstetrics. In 1659, she started her midwifery practice, initially providing free services to impoverished women in her community. Over time, her clientele expanded to include merchant and noble families, earning her a reputation for expertise and skill in her field.
Professional Success and Accusations
Appointed as the City Midwife of Legnica in 1670, Siegemund’s career continued to flourish, culminating in her appointment as the court midwife for the Elector of Brandenburg in 1683. Despite her success, she faced professional challenges, including accusations of unsafe birthing practices. However, her extensive practical knowledge and skill allowed her to successfully defend herself against these allegations, solidifying her place as a respected and trusted figure in the world of midwifery.
- RELATED: Who is Taylor Swift Dating? Navigating the Buzz Around Her and Travis Kelce
- RELATED: Jason Statham Net Worth: The Action Hero’s Earning Punch
- RELATED: Justin Bieber Net Worth: From Street Performer to Millionaire
- RELATED: Elon Musk Net Worth: Evaluating the Wealth of a Space and Tech Tycoon
- RELATED: Cardi B Net Worth: From Stripper to Chart-Topping Rapper
The Court Midwife: A Landmark in Obstetrics
Siegemund’s most notable contribution to the field of midwifery was her seminal work, “The Court Midwife” (1690), a comprehensive obstetrical text that was among the first of its kind written by a woman in Germany. The book presented a systematic and evidence-based approach to various childbirth complications, offering solutions to complex obstetric challenges. Notably, Siegemund introduced innovative techniques such as the two-handed intervention for shoulder presentation deliveries and methods for managing placenta previa.
Legacy and Recognition
Justine Siegemund’s legacy continues to be celebrated, with her work gaining numerous republications and modifications following her passing. Her profound impact on the field of midwifery and women’s healthcare has been acknowledged and honored, most recently with a Google Doodle commemorating her contributions during Women’s History Month in March 2023.

Conclusion
Justine Siegemund’s pioneering spirit, unwavering dedication to her profession, and groundbreaking contributions to the field of midwifery have solidified her place in history as a trailblazing figure. Her unwavering commitment to improving maternal healthcare and her seminal work in obstetrics continue to inspire and empower healthcare professionals and women around the world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Justine Siegemund
- What was Siegemund’s main contribution to midwifery? Siegemund authored the pioneering obstetrical text “The Court Midwife” in 1690, introducing innovative techniques for managing childbirth complications.
- How did Siegemund handle professional challenges? She overcame accusations through her extensive practical knowledge and skill in midwifery, earning respect and trust in her field.
- What impact did Siegemund leave on obstetrics? Her work influenced future advancements in maternal healthcare, leading to several republications and modifications of her text.
- How has Siegemund been honored in recent times? A Google Doodle commemorated her during Women’s History Month in March 2023, highlighting her lasting impact on women’s healthcare.
- What were Siegemund’s key career achievements? She served as the City Midwife of Legnica in 1670 and later as the court midwife for the Elector of Brandenburg, showcasing her expertise in complex childbirth cases.